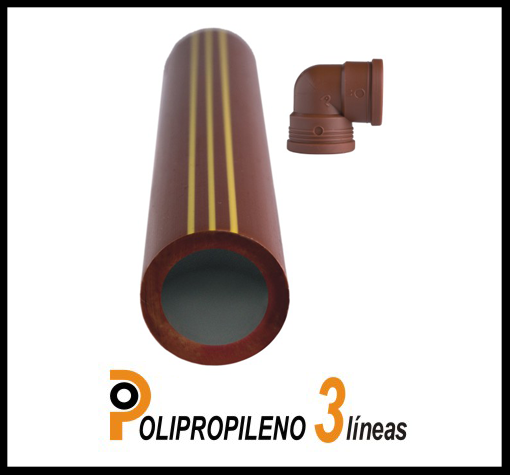
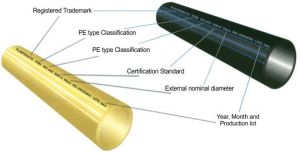
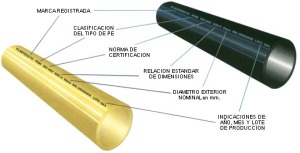
Nets and water distribution
(Transportation of drinkable water and food)
The system fully complies with the European Community requirements (July 1980) and recommendations of WHO, Geneva 1984. UNIT 217, ISO 4427 (1996), UNIT-ISO 4427 (1998) & ISO 8795 (1990).
Gas Distribution
Polyethylene pipes are used in Gas distribution networks for low and medium pressures up to 4 bars. PEMD yellow pipes or black pipes with yellow stripes are used in order to fulfill the signposting requirements for gas pipelines. (ISO 4437, 1997)
Pipeslines and underwater pipelines
One of the great advantages of our pipes is that they are suitable for connections across rivers, channels and lagoons, what can not be done with other products. Sub aquatic connections, buried or over the bed are used to carry drinkable water with pressure, to carry sewage, or for other applications such as protecting Electrical and Phone wires.
Sewer systems, drains, industrial fluid discharge, and buried drainpipes
They are fit for underground applications for sewer systems or draining with no internal service pressure, because they can resist the external load of ground weight and heavy traffic.
To determinate the pipe’s size the following conditions and parameters must be taken into account: ditch’s depth, ground’s density, installation method (compressed), ground’s rigidity (deformation) Plastic deformation ( 50 years, long lifespan), and resistance to heavy traffic whenever it is required.
We highly recommend the use of SDR 33 (or less) pipes , because deformation will always be less than the specified value 6% (recommended for these uses) for a long lasting durability (50 years).
Irrigation and drainage
They can be used for spraying watering, dripping watering and micro spraying watering. An appropriate system of regulation and control can measure out the water and fertilizers.

Relining
(New piping, restoration of damaged pipelines)
Polyethylene pipes are suitable for relining, a technique which consists in introducing another pipe in a damaged pipeline section to restore it or to reinforce its mechanical strength.
This method is used for sewage and drinkable water pipelines, gas conducts, and buried aqueducts.
Transportation of suspended solids
(Mining and dredging)
The pipes resist corrosive and abrasive erosion. They are highly used in hydraulic transportation of solids from sand and crushed stone deposits, in hydraulic and mechanical mining of carbon and minerals
PROTECTION OF CABLES, ELECTRICAL AND PHONE WIRES, AND OPTICAL FIBERS
These pipes have the advantage of being manufactured in coils of any lenght. This is one of the reasons why their use becomes popular for the protection of phone and electrical connections underground, or under water. |
![]()